Code
Code Cell works with information available in eva’s system that doesn’t depend on APIs. It also allows creating variables, that's why it provides immense advantages in a virtual agent flow creation process.
Code cells are very useful in various scenarios, for example:
In ecommerce, the Code cell would be responsible for almost the entire process, such as calculating the number of items or calculating the purchase, etc. Only the chosen products availability search and the finalization of the purchase would be in charge of the Service cell.
Below, to insert in a Code cell, there is an example of code to calculate the value of the purchases in a shopping cart:
var total = 0.0;
if (visibleContext.shoppingCart != null && visibleContext.shoppingCart.items != null) {
for (i in visibleContext.shoppingCart.items)
total += i.price;
}You can also create a simple variable:
hiddenContext.myvar = 5;Or validate user login after a service call:
hiddenContext.logged = trueIn a game, you can simplify a lot the creation of quiz bringing together in a single cell all the questions and answers:
hiddenContext.questions = {
"1": {
"question":"What is the name of the first chatbot ever?",
"answer":"ELIZA"
},
"2": {
"question":"When was ELIZA created?",
"answer":"1966"
}
};.Unlike the Service Cell, which connects data from a company via an API, Code Cell performs many activities (such as calculations and validation) without the need for this connection. This gives you the following advantages:
Manipulate objects
Anticipate executions and actions
Perform services without the need for APIs
Save time
Reduce services costs
How can you create a Code Cell?
Just insert a code snippet in JavaScript as shown in the image below:
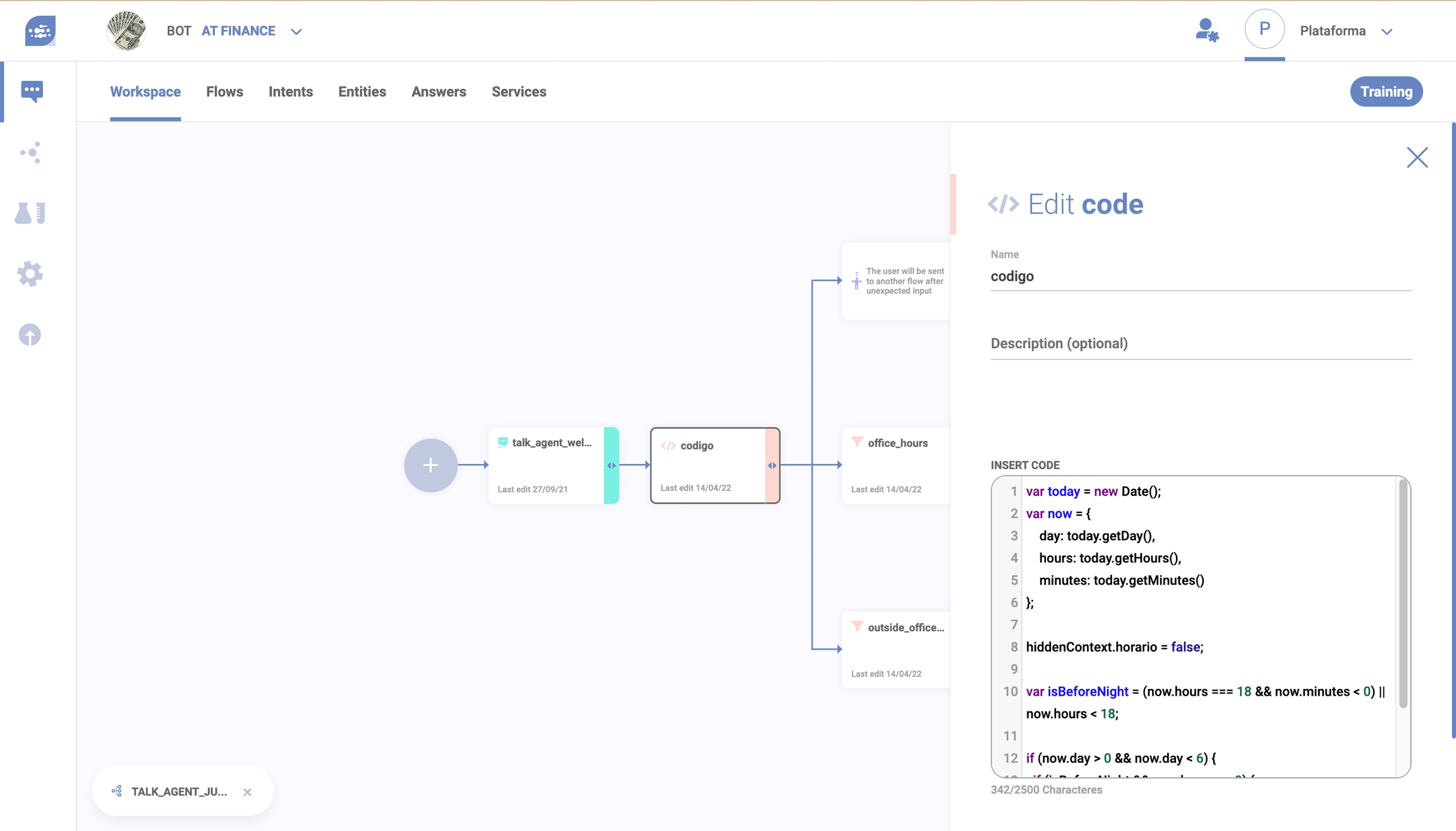
You can use JavaScript’s variables (if you wanna know more about this language, access this page) and program any code in it, as long as it’s executable within 100 milliseconds.
The variables below can be used in eva on the Insert code field:
input
information that users write to the virtual agent and fed into eva
opencontext
information that is open to channels to alter its values
visiblecontext
information that is open to channels, but its values cannot be changed
hiddencontext
information that is closed to channels, being visible only to eva and the services called
intents
information registered in eva that means what the user wants to get out of the interaction. intents[0].name returns the intent name
entities
information registered in eva that means knowledge repositories used by the virtual agent to provide personalized and accurate responses. entities['entity_name'] returns the desired entity.
channelType
channel's type (if it's web, Facebook, Alexa, etc..)
channelName
Channel's name registered in eva
botName
Intent
Name
Type
Required
Description
name
String
Yes
Name of the intent, same as the NLP
confidence
Double
Yes
Confidence score returned by the NLP, this will be a percentage number from 0 to 1.
Entities and intents are read-only attributes. That means you cannot edit their content.
Entity
Name
Type
Required
Description
name
String
Yes
Name of the entity, same as the NLP.
value
String
Yes
The value of the entity returned by the NLP.
position
Position
No
Position of the string within the user input (text).