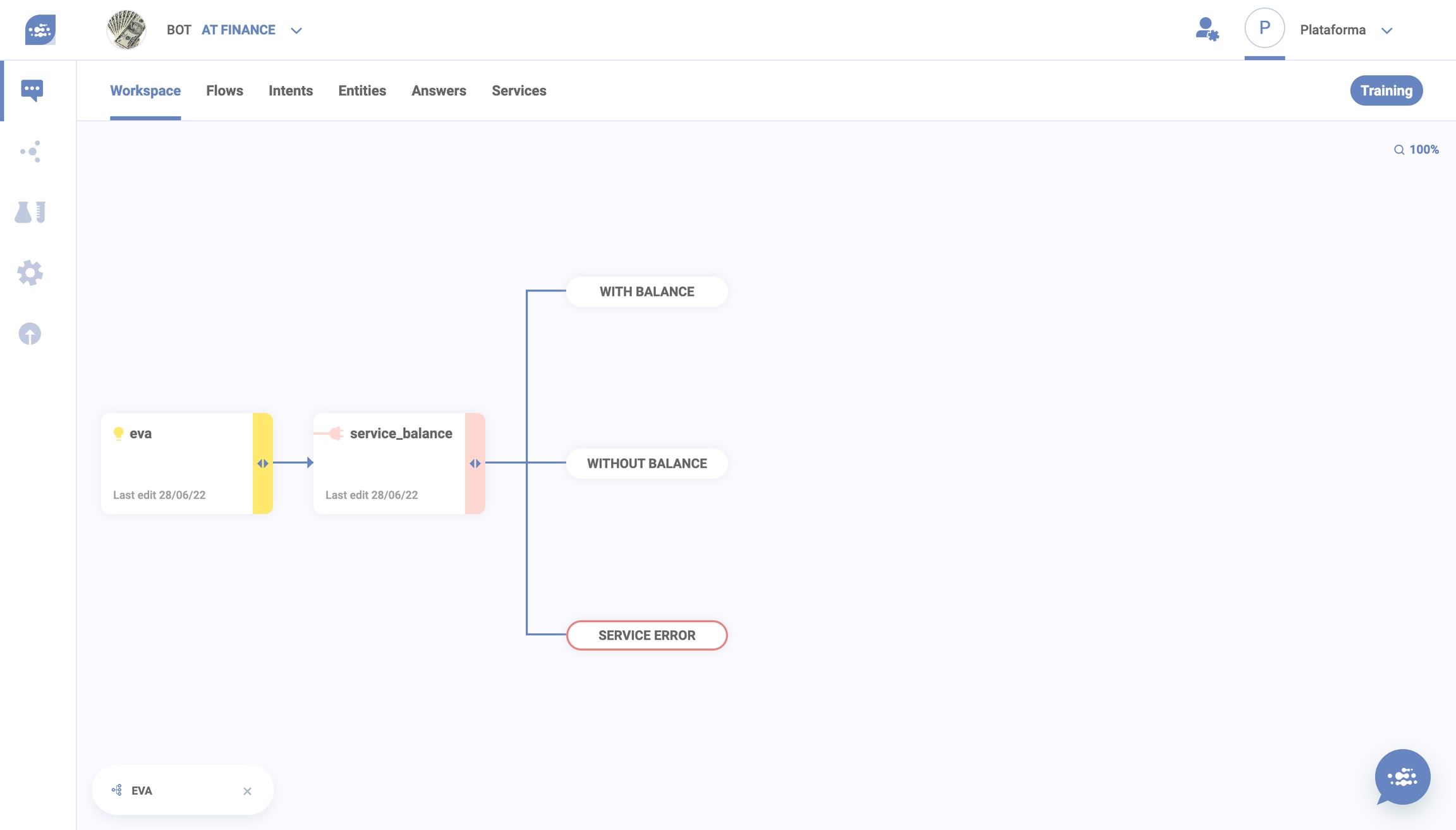
Service

Sometimes you have to look for information outside your knowledge base. To do so, you use a service cell. When you insert a service cell, you are redirecting users to different points in a flow based on options you have created.Services are always connected to an external API through a webhook. When you create a service cell, you redirect users based on their position on an external database.To get more information about:
A good example is sorting users that are registered as clients from users that are not and might be considered prospects.
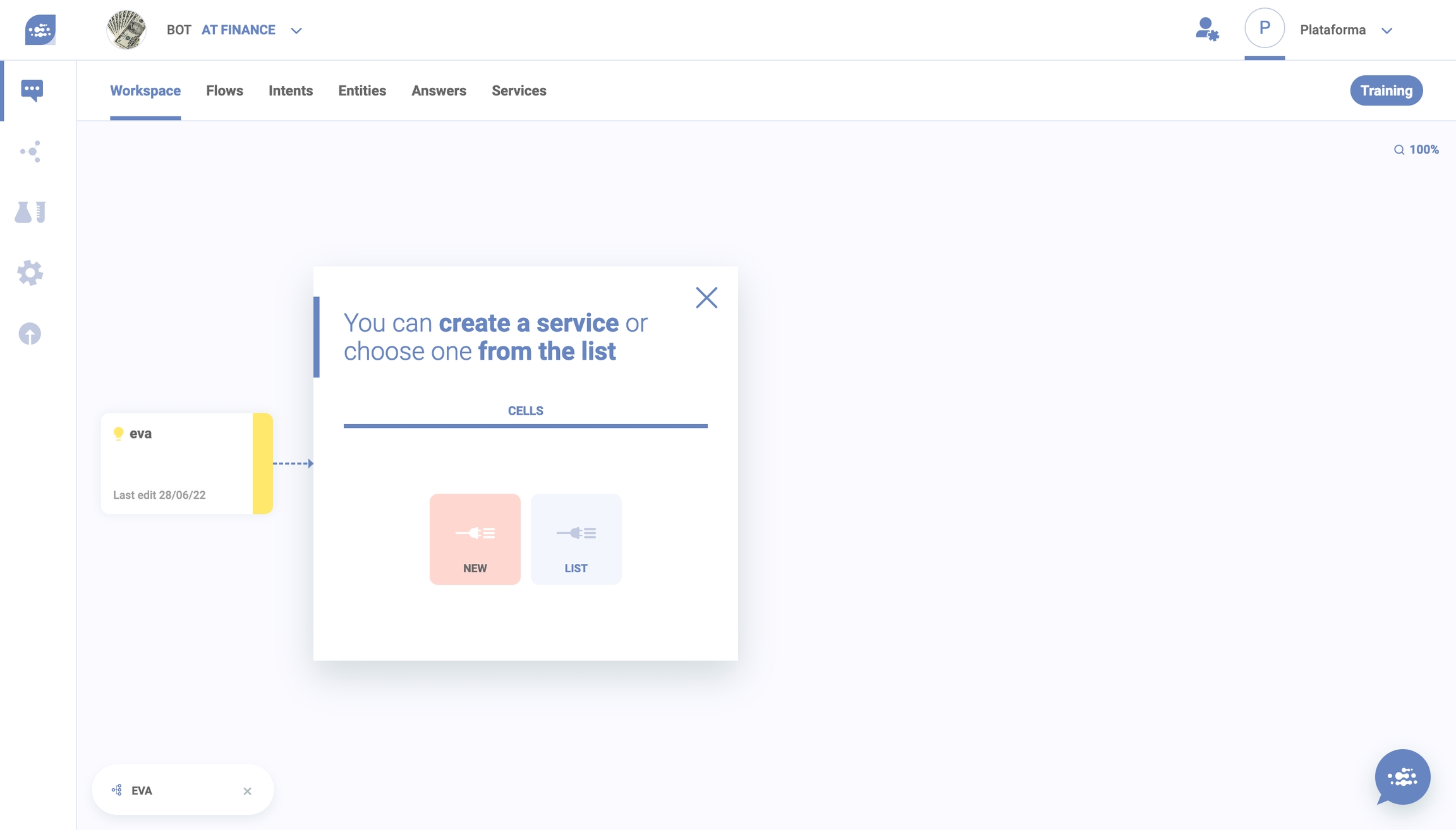
They are automatically saved in the repository when you create them.
To create a service cell, talk to your development team in advance to define what outcomes you are expecting.
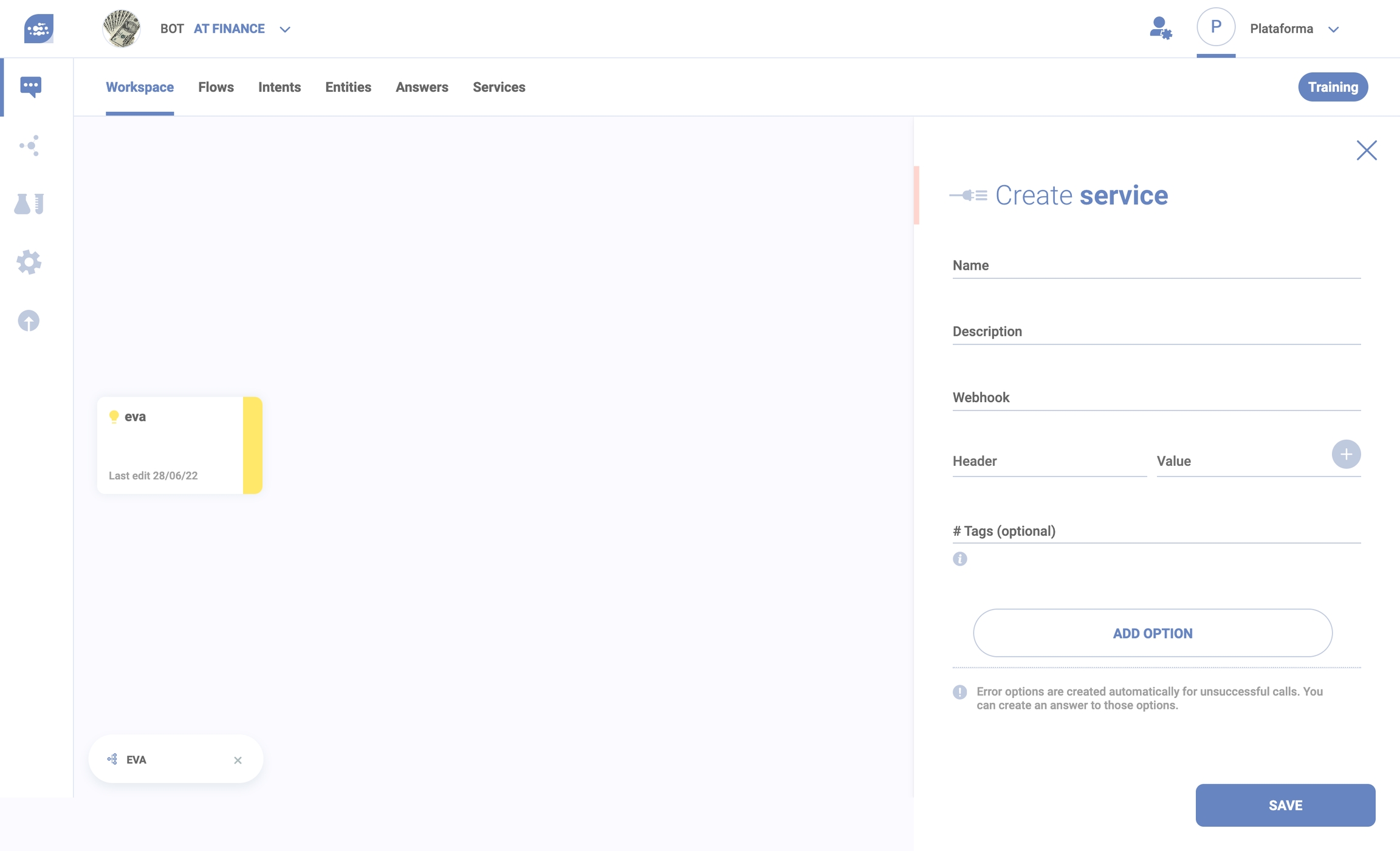
After you click “Create Service”, this modal opens. You have to name it and insert a webhook (an URL that points to an external API following the rules explained in the development manual).
The Header and Value fields can be left blank or a developer can insert a customized header and value.
You can describe it and add up to 5 (five) tags. After that, you can add options. Any created service will be sent to the repository. There, it can be edited or deleted (this actions may have consequences on flows that uses them).
Important: Services don’t share names
After you point where your service cell will look for information, you have to set where your flow will go.
To do so, you have to create options based on what the API will deliver to your virtual agent.
So, after every option, you have to add an answer. They are not buttons, but conditions that have to be met and that allow to disambiguate the flow.
External services might not work. So, eva creates a service error option automatically. As service errors are treated by eva like any other service option, you can add answers after it.