Main Concepts
Main Concepts of Syntphony CAI
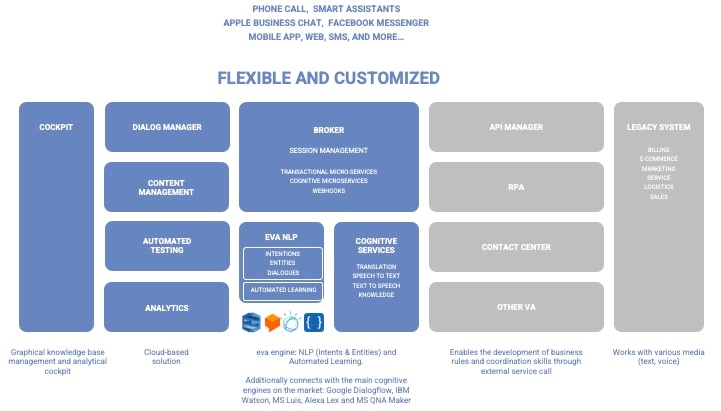
The Dialog Manager is the main feature, the canvas where you create the dialogs and build your virtual agent knowledge base.
These are the main characters in Dialog Manager:
Workspace
Flows
Cells
Training (if you are using Syntphony CAI NLP)
Knowledge AI
Dashboards - Analytics
The Workplace is where you view and design the conversational flows. Here, you will add cells and string them together to give life to the dialog.
Conversational flows consist of cells, which are coordinated elements designated for specific functions within the flow.
Intent
When designing a conversational flow you need to predict the user interactions and the agent responses. An intent cell will represent the users' needs. It is the representation of a user's will, in other words, an action.
Usually it is associated with a verb. Since users can express the same will in different ways, add different examples of how the user would manifest their need.
Entity
Unlike intents, entities are usually associated with an adjective, noun, product, services, etc. In most cases, entities complement intents.
For example, if the the user says: "I want to buy an Apple phone", the terms "cell phone" and "Apple" are the entities (product and brand).
Entities can also represent a very specific user interaction, such as an email. In cases where it is impossible to map all possible user interactions, such as an email list, we design a standardized term that will cater for this type of interaction. And for this we use standard type entity.
Answer
As the name suggests, the Answer cell will answer the user, it's the agent's feedback to an input.
Jump
As the name suggests, the Jump function allows you to go from the last cell created to any other cell in any flow. This is perfect to avoid repetition, as well as shortening and simplifying flows.
Service
Often, an answer to a user demand will require information from an external system or server. For those cases, you can use the transactional cells that allow you to manipulate API calls, such as Webhook, Rest connector and even an transactional answer cell.
Learn more about service cells
Wait-Input
"What is your birth date?", "write your name here", "put your account number here". The Input cell will be responsible for storing this information in the Syntphony CAI. There are three types:
a) Date Template: allows inserting dates. b) Time Template: allows inserting time (hour and minutes) c) Customizable templates: you can enter locations, zip codes, etc.
End
The End eell is the finish line in a flow. By placing this cell in the end, the agent stops communicating at that point. That is, it will only resume the dialog if the user interacts again. The End cell is always used in a Jump flow, never in the User Journey.
Code cell
The Code cell allows you to perform some services without relying on APIs. It offers greater customization. Through the Code cell you can:
Manipulate objects
Route the conversation
Anticipate executions and actions
Perform services without the need for APIs
Reduce time and cost
Rule cell
Use logic and conditions to make your dialog more assertive and much more precise, especially when Intents and Entities can bring up multiple scenarios.
When you connect cells, you create a conversational flow. Create flows with distinct use cases to create your virtual agent. Learn more about flows
Training the virtual agent is important to improve its ability to understand what the user is asking and to be able to answer those questions accurately and efficiently. Training helps the agent learn language patterns, identify intentions and relevant entities, and provide appropriate responses.
The more the agent is trained, the better the results obtained.
More information about training using eva NLP:
Run the dialog to test it out on the dialog simulator. Click the chat widget icon in the bottom right corner. That's where you can simulate the dialog and test the flows.
Last updated